Correctly label the parts of an exocrine gland. – Correctly labeling the parts of an exocrine gland is a crucial aspect of scientific research and medical diagnosis. This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach to labeling the main components of exocrine glands using appropriate anatomical terminology. The accurate identification of these structures is essential for understanding the function and pathology of exocrine glands, enabling advancements in diagnosis, treatment, and drug development.
Exocrine glands are specialized tissues that secrete their products into ducts or onto surfaces. They play diverse roles in the body, including digestion, lubrication, hormone secretion, and immune defense. Understanding the anatomy and function of exocrine glands is fundamental to comprehending their role in health and disease.
Anatomy of Exocrine Glands
Exocrine glands are specialized structures that secrete substances onto the body’s surface or into its cavities. They consist of secretory cells that produce and release the secretory product and duct cells that transport the product to its destination.
Exocrine glands can be classified into three main types based on the nature of their secretory product: serous, mucous, and mixed. Serous glands secrete a thin, watery fluid that contains enzymes, while mucous glands secrete a thick, viscous fluid that contains mucin, a glycoprotein that protects and lubricates surfaces.
Mixed glands secrete both serous and mucous fluids.
Functions of Exocrine Glands
Exocrine glands play a diverse range of functions throughout the body. Some of the most important functions include:
- Digestion: Exocrine glands in the digestive system, such as the salivary glands, stomach glands, and pancreatic glands, secrete enzymes that break down food into smaller molecules for absorption.
- Protection: Exocrine glands in the respiratory and urinary tracts secrete mucus that traps and removes foreign particles and microorganisms.
- Lubrication: Exocrine glands in the eyes, mouth, and joints secrete fluids that reduce friction and protect against wear and tear.
- Hormone secretion: Some exocrine glands, such as the pituitary gland, secrete hormones that regulate various bodily functions.
Labeling the Parts of Exocrine Glands
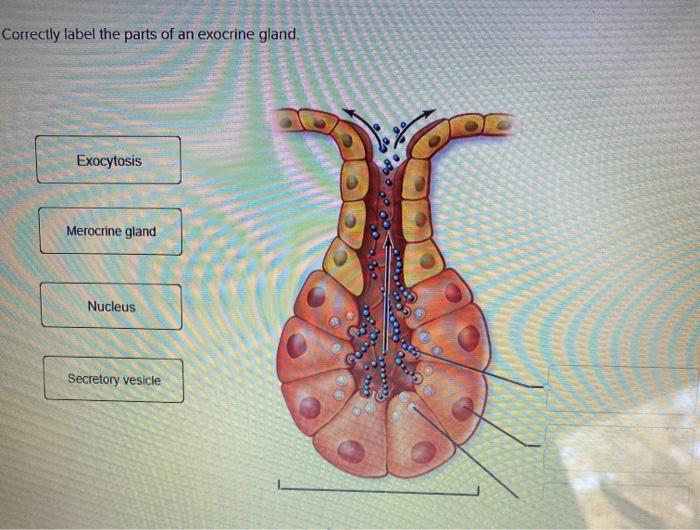
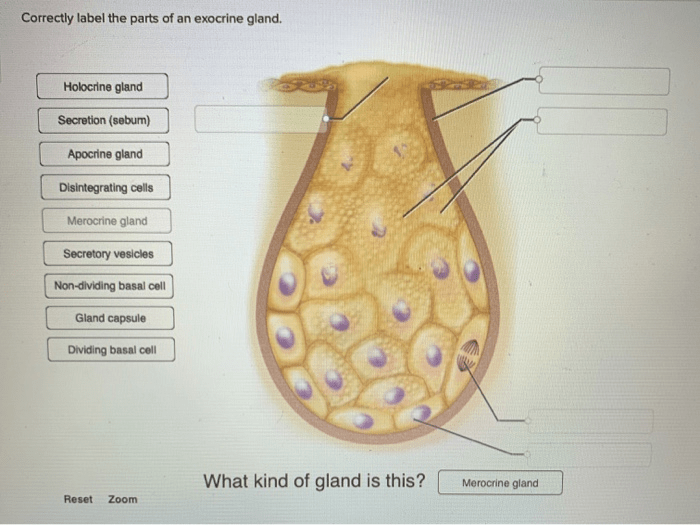
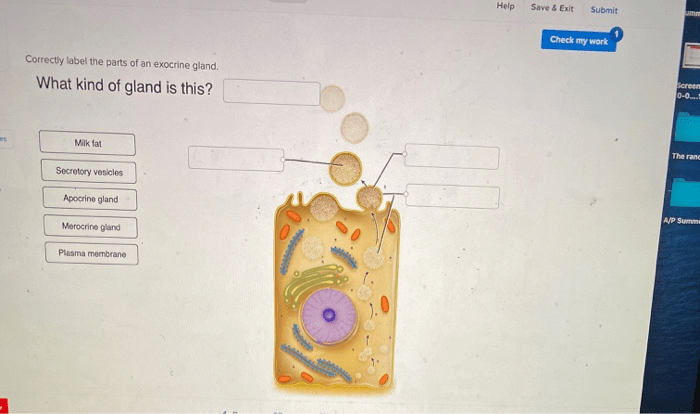
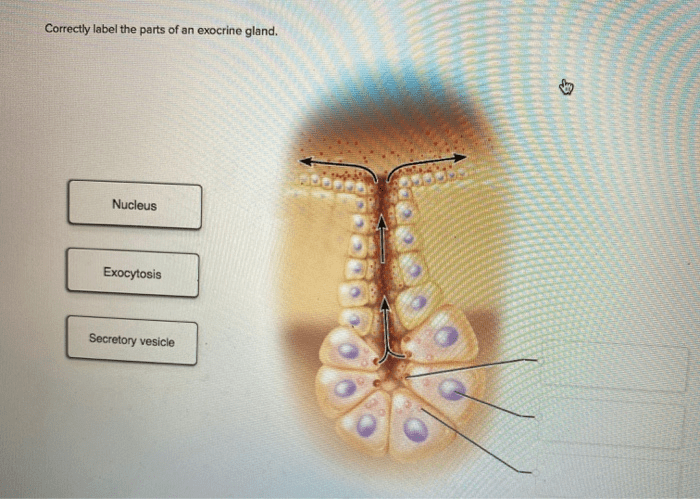
Correctly labeling the parts of exocrine glands is essential for scientific research and medical diagnosis. The main components of exocrine glands include:
- Secretory cells: These cells produce and secrete the gland’s product.
- Duct cells: These cells transport the secretory product to its destination.
- Acini: These are clusters of secretory cells that form the functional units of the gland.
- Ducts: These are channels that transport the secretory product from the acini to the body’s surface or cavity.
Applications of Exocrine Gland Labeling
Exocrine gland labeling has a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Medical diagnosis and treatment of glandular disorders: Labeling exocrine glands can help diagnose and treat conditions such as pancreatitis, sialadenitis, and prostate cancer.
- Histological analysis of tissue samples: Labeling exocrine glands can help identify and characterize different types of cells and tissues in tissue samples.
- Pharmaceutical development and drug testing: Labeling exocrine glands can help evaluate the effects of drugs on glandular function and secretion.
Emerging Techniques in Exocrine Gland Labeling, Correctly label the parts of an exocrine gland.
Emerging techniques for labeling exocrine glands include:
- Fluorescent labeling: This technique uses fluorescent dyes to label exocrine glands for visualization in microscopy.
- Immunohistochemistry: This technique uses antibodies to label specific proteins within exocrine glands.
- Electron microscopy: This technique uses a beam of electrons to create detailed images of exocrine glands at the ultrastructural level.
Detailed FAQs: Correctly Label The Parts Of An Exocrine Gland.
What is the importance of correctly labeling the parts of an exocrine gland?
Correctly labeling the parts of an exocrine gland is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment of glandular disorders. It also facilitates histological analysis of tissue samples and enables the development and testing of drugs that target specific components of exocrine glands.
What are the main components of an exocrine gland?
The main components of an exocrine gland include the secretory cells, ducts, and acini. Secretory cells produce and secrete the gland’s product, while ducts transport the secretion to the surface or into a cavity.
What are the different types of exocrine glands?
Exocrine glands are classified into three main types based on the nature of their secretion: serous, mucous, and mixed glands. Serous glands secrete a watery fluid, mucous glands secrete a thick, viscous substance, and mixed glands secrete a combination of both.