Welcome to the fascinating realm of arithmetic sequences, where patterns dance and numbers reveal hidden relationships. Arithmetic sequences quiz part 1 embarks on a journey of discovery, unlocking the secrets of these enigmatic progressions.
As we delve into the intricacies of arithmetic sequences, we will uncover their defining characteristics, explore the common difference, and unravel the power of explicit and recursive formulas. Through engaging examples and step-by-step explanations, this quiz will challenge your understanding and sharpen your problem-solving skills.
Introduction
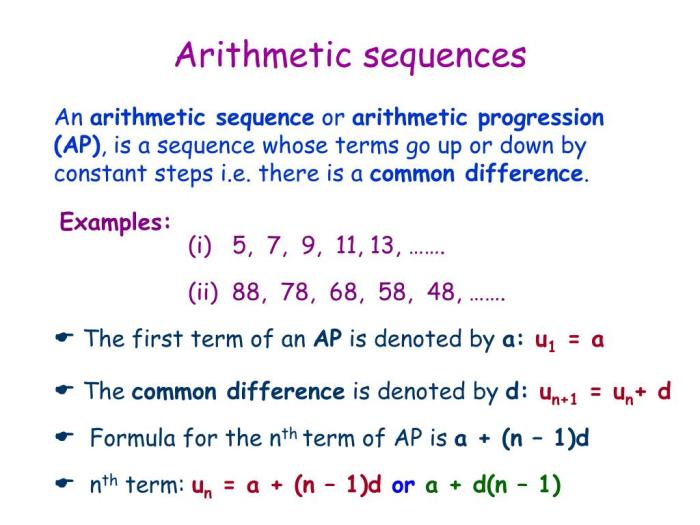
Arithmetic sequences are a type of number sequence in which the difference between any two consecutive terms is the same. This constant difference is called the common difference.
For example, the sequence 2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 17 is an arithmetic sequence with a common difference of 3. The difference between any two consecutive terms, such as 5 – 2 or 11 – 8, is always 3.
Importance of Arithmetic Sequences, Arithmetic sequences quiz part 1
Arithmetic sequences are important in mathematics because they can be used to model many real-world phenomena. For example, the motion of a falling object can be modeled as an arithmetic sequence, where the common difference represents the acceleration due to gravity.
Common Difference
In an arithmetic sequence, the common difference is the constant value by which each term differs from its preceding term. It is denoted by ‘d’.
To find the common difference, we can subtract any term from its subsequent term. For example, in the sequence 2, 5, 8, 11, 14, the common difference is 3 because each term is 3 more than the previous term.
Finding the Common Difference
To find the common difference, follow these steps:
- Choose any two consecutive terms in the sequence, let’s say anand an+1.
- Subtract the first term from the second term: an+1
.an
- The result is the common difference, ‘d’.
For example, in the sequence 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, the common difference is 5 because an+1– a n= 15 – 10 = 20 – 15 = 25 – 20 = 30 – 25 = 5 .
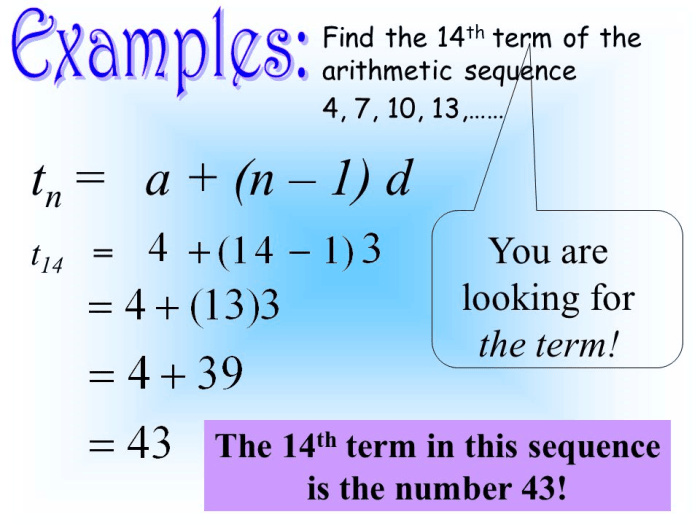
Explicit Formula
An arithmetic sequence is a sequence of numbers in which the difference between any two consecutive terms is constant. The explicit formula for an arithmetic sequence is a formula that gives the value of any term in the sequence, given the value of the first term and the common difference.
The explicit formula for an arithmetic sequence is:
$$a_n = a_1 + (n
1)d$$
where:
- $a_n$ is the nth term of the sequence
- $a_1$ is the first term of the sequence
- $d$ is the common difference
- $n$ is the number of the term you want to find
Examples
For example, if the first term of an arithmetic sequence is 3 and the common difference is 5, then the explicit formula for the sequence is:
$$a_n = 3 + (n
1)5$$
To find the 10th term of the sequence, we can substitute n = 10 into the explicit formula:
$$a_10 = 3 + (10
1)5 = 3 + 9(5) = 52$$
Limitations
The explicit formula for an arithmetic sequence is only valid for finding the value of a specific term in the sequence. It cannot be used to find the sum of the sequence or to determine whether the sequence is convergent or divergent.
4. Recursive Formula
An arithmetic sequence can also be defined recursively, meaning that each term is defined in terms of the previous term. The recursive formula for an arithmetic sequence is:
an= a n-1+ d
where a nis the nth term, a n-1is the (n-1)th term, and d is the common difference.
Example
Find the 5th term of the arithmetic sequence 2, 5, 8, 11, …
Using the recursive formula, we have:
a5= a 4+ d = 11 + 3 = 14
Therefore, the 5th term is 14.
Advantages of the Recursive Formula
The recursive formula has several advantages over the explicit formula. First, it is easier to remember and apply. Second, it can be used to generate terms of an arithmetic sequence even if we do not know the first term or the common difference.
Arithmetic Sequence Problems
Arithmetic sequence problems involve finding the unknown terms or properties of an arithmetic sequence given specific information. Solving these problems requires a systematic approach and an understanding of the concepts of arithmetic sequences.
To solve arithmetic sequence problems, follow these steps:
- Identify the given information, including the first term, common difference, or explicit formula.
- Determine what is being asked, whether it’s a specific term, the common difference, or a general formula.
- Apply the appropriate formula or concept to solve the problem.
- Check your answer to ensure it satisfies the given conditions.
Sample Quiz Questions
The following table provides a sample quiz with various types of arithmetic sequence problems:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Find the 10th term of the arithmetic sequence 2, 5, 8, 11, … | 29 |
Find the common difference of the arithmetic sequence
|
3 |
| Write the explicit formula for the arithmetic sequence 10, 15, 20, 25, … | an= 10 + 5(n
|
| Find the sum of the first 15 terms of the arithmetic sequence 6, 10, 14, 18, … | 360 |
| Determine if the sequence 5, 10, 17, 26, … is an arithmetic sequence. If so, find its common difference. | Yes; common difference is 7 |
Applications of Arithmetic Sequences: Arithmetic Sequences Quiz Part 1
Arithmetic sequences find applications in various fields, including physics, finance, and everyday life.
In physics, arithmetic sequences are used to model uniformly accelerated motion. The distance traveled by an object in uniformly accelerated motion is given by the formula:
$$d = ut + 1/2 at^2$$
where:
- d is the distance traveled
- u is the initial velocity
- a is the acceleration
- t is the time
This formula can be expressed as an arithmetic sequence with the common difference being:
$$a = 1/2 at^2$$
In finance, arithmetic sequences are used to model the growth of investments. The future value of an investment is given by the formula:
$$FV = PV(1 + r)^n$$
where:
- FV is the future value
- PV is the present value
- r is the annual interest rate
- n is the number of years
This formula can be expressed as an arithmetic sequence with the common difference being:
$$r = (1 + r)
1$$
Arithmetic sequences are also used in everyday life to model a variety of phenomena, such as the growth of bacteria, the decay of radioactive isotopes, and the spread of rumors.
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Physics | Modeling uniformly accelerated motion |
| Finance | Modeling the growth of investments |
| Everyday life | Modeling the growth of bacteria, the decay of radioactive isotopes, and the spread of rumors |
Clarifying Questions
What is the common difference of an arithmetic sequence?
The common difference is the constant value added to each term to obtain the next term in the sequence.
How do I use the explicit formula for an arithmetic sequence?
The explicit formula is given by an = a1 + (n – 1)d, where a1 is the first term, n is the term number, and d is the common difference.
What are the advantages of using the recursive formula for an arithmetic sequence?
The recursive formula is useful when the first term and common difference are known, as it allows us to generate subsequent terms without having to know the explicit formula.