Chest compression feedback device monitors what – Chest compression feedback devices play a crucial role in enhancing the quality of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) by providing real-time feedback on the effectiveness of chest compressions. These devices monitor key parameters during CPR, enabling healthcare professionals to optimize compression depth, rate, and recoil, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
This article explores the various types of chest compression feedback devices, the parameters they monitor, and how they provide guidance to users. It also discusses the accuracy, reliability, benefits, and applications of these devices, as well as potential advancements and innovations in this field.
Definition and Overview of Chest Compression Feedback Devices
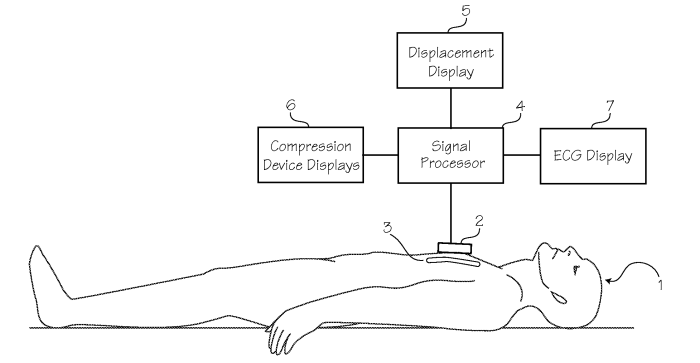
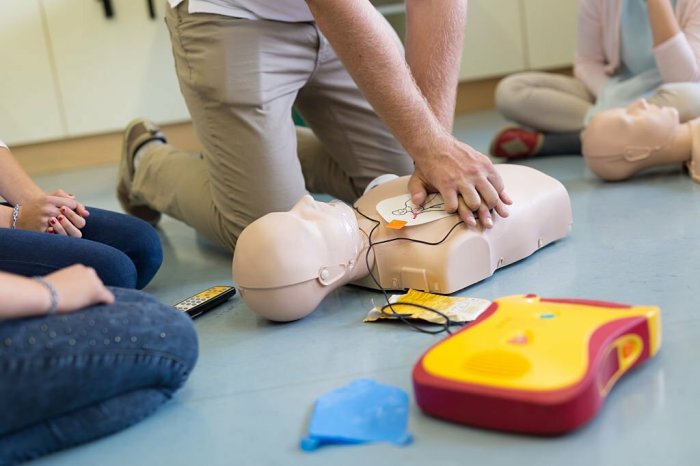
Chest compression feedback devices are electronic devices that provide real-time feedback to users during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). They monitor various parameters of chest compressions and provide guidance to ensure that compressions are performed effectively and according to established guidelines. These devices play a crucial role in improving the quality and effectiveness of CPR, increasing the chances of survival for cardiac arrest victims.
Types of Chest Compression Feedback Devices, Chest compression feedback device monitors what
There are two main types of chest compression feedback devices:
- Load-based devices:Measure the force applied to the chest during compressions and provide feedback on the depth and rate of compressions.
- Impedance-based devices:Measure the electrical impedance of the chest and use this data to estimate the depth and rate of compressions.
Monitoring Parameters
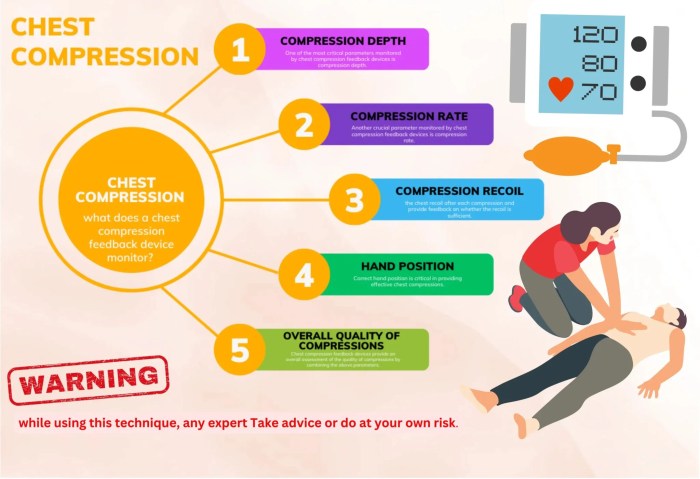
Chest compression feedback devices typically monitor the following parameters:
- Compression depth:The depth of the chest compressions, measured in millimeters.
- Compression rate:The rate of the chest compressions, measured in compressions per minute.
- Time to compression:The time it takes from the initiation of the compression to the moment the chest is fully compressed.
- Release time:The time it takes from the end of the compression to the moment the chest is fully released.
- Compression fraction:The percentage of time during which the chest is compressed.
Real-Time Feedback and Guidance
Chest compression feedback devices provide real-time feedback to users through various mechanisms:
- Visual feedback:Displays on a screen or LED indicators that provide information on compression depth, rate, and other parameters.
- Audible feedback:Uses sounds or voice prompts to guide users on the correct compression technique.
- Haptic feedback:Provides physical cues, such as vibrations or pulses, to indicate the correct depth and rate of compressions.
Accuracy and Reliability: Chest Compression Feedback Device Monitors What
The accuracy and reliability of chest compression feedback devices are crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of CPR. Factors that can affect the accuracy of these devices include:
- Chest anatomy:The shape and size of the patient’s chest can affect the accuracy of compression depth measurements.
- Patient position:The patient’s position on the surface can affect the accuracy of compression rate measurements.
- Device placement:The placement of the device on the patient’s chest can affect the accuracy of both depth and rate measurements.
Benefits and Applications
The use of chest compression feedback devices offers several benefits:
- Improved compression quality:Feedback devices help users perform compressions that meet the recommended depth and rate guidelines.
- Increased survival rates:Studies have shown that the use of feedback devices is associated with increased survival rates in cardiac arrest patients.
- Reduced fatigue:Feedback devices can help users avoid excessive fatigue during CPR, ensuring that compressions can be sustained for a longer period.
Chest compression feedback devices are widely used in various settings, including:
- Emergency medical services (EMS)
- Hospitals
- Nursing homes
- Community CPR training programs
Design and Development

The design and development of chest compression feedback devices involve several challenges and considerations:
- Accuracy and reliability:Ensuring that the device accurately measures compression parameters is paramount.
- Ease of use:The device should be easy to use for both trained and untrained users.
- Durability:The device should be able to withstand the rigors of CPR, including repeated use and exposure to fluids.
- Cost-effectiveness:The device should be affordable and accessible to a wide range of users.
Future Advancements and Innovations
The field of chest compression feedback devices is continuously evolving, with new advancements and innovations emerging:
- Integration with other CPR devices:Feedback devices are being integrated with other CPR devices, such as automated external defibrillators (AEDs), to provide a comprehensive CPR solution.
- Artificial intelligence (AI):AI is being used to improve the accuracy and reliability of feedback devices by analyzing data and providing real-time guidance.
- Wearable devices:Wearable chest compression feedback devices are being developed for use in real-time monitoring during CPR.
These advancements promise to further enhance the effectiveness and accessibility of CPR, improving the chances of survival for cardiac arrest victims.
Quick FAQs
What are the key parameters monitored by chest compression feedback devices?
Chest compression feedback devices typically monitor compression depth, rate, and recoil.
How do chest compression feedback devices provide feedback to users?
Feedback can be provided through visual displays, audible cues, or tactile feedback, guiding users to adjust their compression technique.
What are the benefits of using chest compression feedback devices?
Benefits include improved compression quality, reduced variability between providers, and increased user confidence.