Delving into AP English Language Rhetorical Devices, this guide immerses readers in a comprehensive exploration of the persuasive techniques that elevate writing to new heights. Rhetorical devices, the tools of persuasion, empower writers to shape meaning, evoke emotions, and drive action.
From metaphors to parallelism, this guide unravels the intricacies of these linguistic tools, providing a roadmap for their effective use in essays, speeches, and literary works.
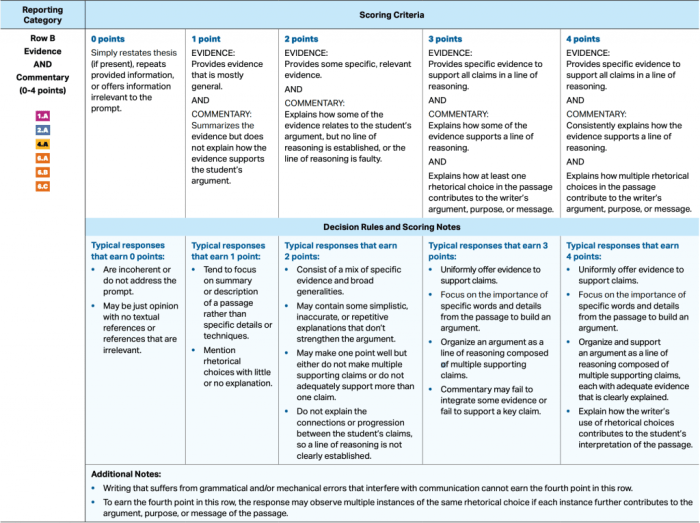
Types of Rhetorical Devices: Ap English Language Rhetorical Devices

Rhetorical devices are literary techniques that enhance the effectiveness of written and spoken communication. They are employed to persuade, inform, and entertain an audience. In AP English Language and Composition, a comprehensive understanding of rhetorical devices is essential for students to analyze and produce sophisticated writing.
The following is a comprehensive list of rhetorical devices commonly used in AP English Language:
- Anaphora: Repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of successive phrases, clauses, or sentences.
- Antithesis: Contrast of two opposing ideas or concepts.
- Apostrophe: Direct address to an absent person or object.
- Asyndeton: Omission of conjunctions between words, phrases, or clauses.
- Chiasmus: Reversal of the order of words or phrases in parallel clauses.
- Epanalepsis: Repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning and end of a clause or sentence.
- Epistrophe: Repetition of a word or phrase at the end of successive phrases, clauses, or sentences.
- Hyperbole: Exaggeration for emphasis.
- Irony: Expression of the opposite of what is meant.
- Metaphor: Comparison of two unlike things without using “like” or “as.”
- Metonymy: Substitution of a closely related word or phrase for the original term.
- Oxymoron: Combination of two contradictory terms.
- Paradox: Statement that seems contradictory but may contain a deeper truth.
- Personification: Giving human qualities to nonhuman things.
- Polysyndeton: Excessive use of conjunctions between words, phrases, or clauses.
- Simile: Comparison of two unlike things using “like” or “as.”
- Synecdoche: Use of a part to represent the whole or vice versa.
- Understatement: Deliberate minimization of the importance of something.
FAQ Resource
What are rhetorical devices?
Rhetorical devices are linguistic techniques used to enhance the persuasive impact of writing. They employ figurative language, structural patterns, and other strategies to create vivid imagery, evoke emotions, and drive action.
How can I use rhetorical devices effectively?
To use rhetorical devices effectively, choose devices that align with your writing purpose and audience. Integrate them seamlessly into your writing, ensuring they enhance clarity, persuasion, and impact without overwhelming the reader.
What are some common rhetorical devices?
Common rhetorical devices include metaphors, similes, personification, hyperbole, and parallelism. Each device serves a unique purpose, from creating vivid imagery to establishing logical connections.