Pltw activity 1.1 1 answer key – Embark on a captivating journey with the PLTW Activity 1.1.1 Answer Key, your ultimate guide to STEM exploration. This comprehensive resource unveils the secrets of the activity, empowering you to unlock the wonders of science, technology, engineering, and math.
Step into the realm of PLTW, where hands-on learning meets real-world applications. With this answer key by your side, you’ll navigate the activity with ease, unraveling the complexities of STEM concepts and fostering a deep understanding of their practical relevance.
Introduction
PLTW Activity 1.1.1, titled “Introduction to the Design Process,” is an introductory activity that sets the stage for the Project Lead The Way (PLTW) Engineering Design and Development curriculum. This activity introduces students to the engineering design process, a systematic and iterative approach used to solve engineering problems.
The purpose of this activity is to provide students with a foundational understanding of the engineering design process and its key elements. Through hands-on activities and discussions, students will learn about the different phases of the design process, including problem definition, research, brainstorming, prototyping, testing, and evaluation.
Activity Procedures: Pltw Activity 1.1 1 Answer Key
The activity involves several steps to guide you through the exploration of the engineering design process.
You will be provided with the necessary materials and equipment, including:
- Building materials (e.g., cardboard, straws, tape)
- Design tools (e.g., rulers, protractors, graph paper)
- Testing equipment (e.g., weights, force gauges)
Design Phase
In this phase, you will:
- Identify the problem or need.
- Research and gather information.
- Develop and sketch multiple design ideas.
- Select the best design based on criteria and constraints.
Build Phase
Once the design is finalized, you will:
- Gather the necessary materials.
- Follow the design plans to construct the prototype.
- Make adjustments or modifications as needed.
Test and Evaluate Phase, Pltw activity 1.1 1 answer key
In this phase, you will:
- Develop a testing plan to evaluate the prototype’s performance.
- Conduct experiments and collect data.
- Analyze the data and make observations.
- Identify areas for improvement.
Improve and Redesign Phase
Based on the test results, you will:
- Make necessary modifications to the design.
- Rebuild and retest the prototype.
- Repeat the testing and evaluation process until the desired performance is achieved.
Data Collection and Analysis
Now that you have a research question, it’s time to gather data to answer it. Data collection is the process of gathering and measuring information on variables of interest, in an established systematic fashion that enables one to answer stated research questions, test hypotheses, and evaluate outcomes.
The data you collect should be relevant to your research question and should be collected in a way that minimizes bias. Once you have collected your data, you need to analyze it to draw conclusions. Data analysis is the process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of highlighting useful information, suggesting conclusions, and supporting decision-making.
Organizing and Analyzing Data
There are many different ways to organize and analyze data. The best method will depend on the type of data you have and the research question you are trying to answer. Some common methods of data analysis include:
- Descriptive statistics: These statistics describe the basic features of your data, such as the mean, median, and mode.
- Inferential statistics: These statistics allow you to make inferences about a population based on a sample.
- Data visualization: This involves creating graphs and charts to help you visualize your data and identify patterns.
Once you have analyzed your data, you need to draw conclusions. Your conclusions should be based on the evidence that you have collected and should be clearly stated.
Activity Modifications
To accommodate diverse learning styles, consider the following modifications:
Differentiation by Grade Level
- For lower grade levels, simplify the instructions and provide more hands-on support.
- For higher grade levels, introduce more complex concepts and challenge students with open-ended questions.
Differentiation by Learning Style
- For visual learners, provide diagrams and graphic organizers.
- For auditory learners, use verbal explanations and discussions.
- For kinesthetic learners, incorporate hands-on activities and experiments.
- For logical learners, emphasize the logical connections between concepts.
Extensions
This activity can be extended beyond the classroom to reinforce learning and connect it to real-world applications.
Finished up with PLTW Activity 1.1 1 and looking for some more practice? Why not take a break and check out the AP Lang Unit 4 Progress Check ? It’s a great way to test your understanding of the concepts covered in the unit so far.
Once you’re done, come back and finish up with PLTW Activity 1.1 1.
Consider these ideas for extending the activity:
Connecting to Other Subject Areas
- Science:Students can explore the scientific principles behind the design and function of the bridge, including the concepts of force, balance, and structural integrity.
- Math:Students can apply their knowledge of geometry and measurement to calculate the dimensions and angles of the bridge.
- Art:Students can use their creativity to design and decorate their bridges, incorporating elements of color, texture, and shape.
Real-World Applications
- Engineering:Students can learn about the role of engineers in designing and constructing bridges, and explore different types of bridges used in the real world.
- Architecture:Students can examine the architectural features of bridges, such as their shape, materials, and ornamentation, and discuss how these elements contribute to the overall design.
li> History:Students can research famous bridges from around the world and explore their historical significance and impact on society.
Troubleshooting
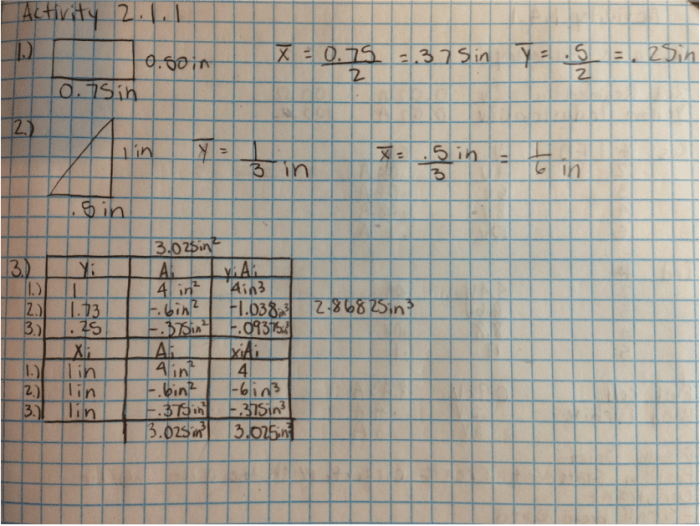
As students engage in this activity, they may encounter various challenges. Here are some common issues and troubleshooting tips to assist them:
Troubleshooting Data Collection
- Problem:Students have difficulty identifying or measuring the variables accurately.
- Tip:Review the activity instructions thoroughly and ensure students understand the definitions and measurement techniques for each variable.
- Problem:Students struggle to obtain consistent data.
- Tip:Emphasize the importance of following the experimental procedure precisely and using appropriate measuring tools.
- Problem:Students encounter outliers or unexpected data.
- Tip:Encourage students to repeat measurements or consider potential sources of error, such as measurement inaccuracies or environmental factors.
Troubleshooting Data Analysis
- Problem:Students have difficulty interpreting the data or drawing conclusions.
- Tip:Guide students through the analysis process step by step, emphasizing the relationship between the variables and the patterns observed.
- Problem:Students struggle to apply the results to real-world scenarios.
- Tip:Provide examples or discuss applications of the concepts being explored in the activity to make the learning more relatable.
Troubleshooting Experimental Design
- Problem:Students make design errors that affect the validity of their results.
- Tip:Review the principles of experimental design, such as controlling variables and using appropriate sample sizes, to ensure students understand the importance of these aspects.
Assessment
Evaluating student learning is crucial in this activity. Teachers can assess students’ understanding through various methods, including:
- Class Participation:Observing students’ engagement, asking questions, and contributing to discussions.
- Quizzes:Short assessments to test students’ knowledge and understanding of key concepts.
- Projects:Assigning students to create projects that demonstrate their learning and creativity.
- Presentations:Having students present their findings or ideas to the class, fostering their communication skills.
- Portfolios:Collecting student work throughout the activity to assess their progress and growth.
Rubrics and Grading Criteria
To ensure fair and consistent assessment, teachers should develop rubrics or grading criteria. These rubrics should clearly Artikel the expectations for each assessment task, including:
- Learning Objectives:The specific skills or knowledge that students are expected to demonstrate.
- Levels of Performance:The different levels of proficiency students can achieve, such as proficient, developing, or needs improvement.
- Assessment Criteria:The specific aspects of the task that will be evaluated, such as accuracy, completeness, and creativity.
- Scoring Guide:The point values or grades assigned to each level of performance for each criterion.
By using rubrics or grading criteria, teachers can provide students with clear feedback on their strengths and areas for improvement, fostering their learning and growth.
Essential FAQs
What is the purpose of the PLTW Activity 1.1.1?
To provide students with hands-on experience in STEM concepts, fostering their understanding and application of these principles.
What materials are required for the activity?
Materials vary depending on the specific activity, but typically include items such as building materials, sensors, and electronic components.
How can I use the answer key effectively?
Use the answer key as a reference guide to check your work, identify areas for improvement, and gain insights into the correct solutions.